Key Applications
Nitriding
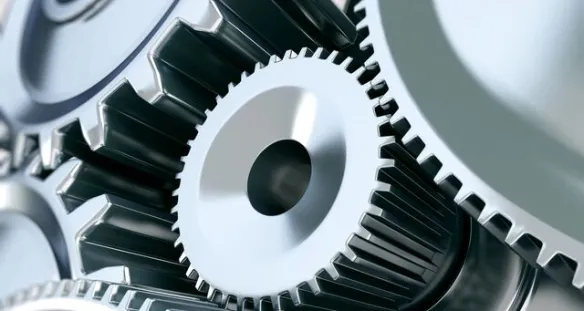
Ammonia gas is widely used in nitriding, a heat treatment process designed to harden the surface of steel and other alloys. The process involves heating the metal in an atmosphere of ammonia gas, which dissociates into nitrogen and hydrogen. The nitrogen atoms then diffuse into the surface of the metal, forming hard nitrides that improve wear resistance, fatigue strength, and corrosion resistance. Nitriding is commonly used in the automotive and aerospace industries for components such as gears, shafts, and engine parts.
Nitro-Carburizing

Nitro-carburizing is a surface hardening process similar to nitriding, but it also incorporates carbon into the surface of the metal. Ammonia gas is used to generate a nitrogen-rich environment, while the process also introduces carbon from gases like carbon monoxide or methane. This treatment enhances both wear resistance and fatigue strength, while also improving corrosion resistance. Nitro-carburizing is often used in applications where a combination of hard, wear-resistant surface and good corrosion resistance is required, such as in automotive components, firearm parts, and industrial machinery.
Process Control & Atmosphere Generation

Ammonia gas is also used in various industrial processes as part of controlled atmospheres. In the chemical industry, it’s involved in the production of fertilizers, such as ammonium nitrate, which relies on ammonia as a key feedstock. Similarly, ammonia plays a role in the production of other chemicals like urea and hydrogen, making it indispensable in the synthesis of many materials essential for industries such as agriculture, energy, and manufacturing.
Find your safety data sheet
Safety Documentation
Gas safety data sheets (MSDS)
Find the reference document you need.
Find your local Energas branch or Agent
Do you have any questions about Ammonia gas?
Please complete our contact form below and we'll come back to you as soon as possible.

