TIG Welding Gas
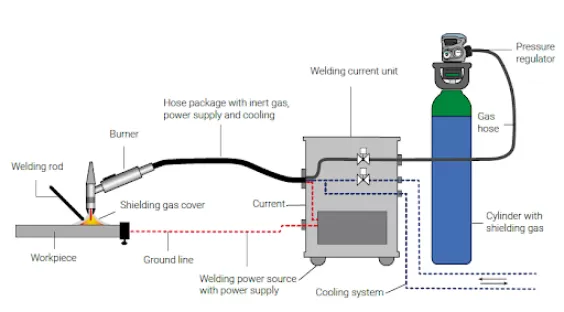
TIG or tungsten inert gas welding, also known as gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), is a very stable arc welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode and an inert gas to create high-quality welds. Depending on the project, the use of filler metal is optional for TIG welding.
TIG welding is applied in all industrial sectors but it is mainly used in apparatus and pipeline construction in the chemical and food industries . When feeding filler rods to the weld pool, TIG welders have to use both hands at the same time. All this makes TIG welding a far more challenging process than MIG/MAG, where the filler wire is automatically fed from the welding torch.
TIG welding is operated with a drooping constant current power source (DC or AC). In DC the tungsten electrode is always negative polarity to prevent overheating and melting. AC is used when welding materials with a tenacious oxide film, such as aluminium. Electrodes for TIG welding are normally pure tungsten with rare earth metal oxides (cerium, lanthanum, zirconia) give superior performance.
In TIG welding Argon is the most commonly used shielding gas which can be used for welding a wide range of materials including steel, stainless steel, aluminium and titanium. Argon mixed with Helium or Hydrogen or Nitrogen can also be used depending on the material to be welded. Energas have a wide range of high quality welding gases for TIG welding including ARCAL™ Prime for Pure Argon and Argon mixtures to suit all operational and welding. material needs.
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|
| Argon (Ar) |
|
|
| Helium (He) |
|
|
| Nitrogen (N2) |
| |
| Hydrogen (H2) |
|
|
Welding gas selector guide

Helping you choose the right gas for your welding needs.
Select your material, welding type, wire type and material thickness and the tool which highlight our specific welding mixture suitable for your welding application.
Do you have any questions about TIG Welding?
Please complete our contact form below and we'll come back to you as soon as possible.
More information
ISO14175 compliant welding gases
Frequently Asked Questions:
How to choose which gas to use in MIG or MAG?
What is the difference between the MIG and MAG welding processes?
What is the difference between brazing and welding?
How to adjust the gas flow when welding?
